round coffee table,luxury coffee table,coffee table set luxury modern,stone coffee table Kumusi (Dongguan) Furniture Co., Ltd. , https://www.coombesfurniture.com
Use of gene guns in aseptic workstations
**Equipment and Materials**
1. GDS-80 gene gun with 4.5 mm barrel, pressure regulator, and hose (WGB09O001) (Wealtec)
2. Aseptic bench
3. 3 cm target spacer (Wealtec)
4. Purity 99.999% helium gas
5. Sample: Zea mays L. embryos
**Experimental Procedure**
1. Before starting the experiment, adjust the output pressure of the GDS-80 gene gun according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure even particle distribution. After setting the parameters, clean the sample cannula and barrel with 70% ethanol to maintain sterility.
2. Thoroughly clean and disinfect the aseptic bench before use. UV exposure for at least 30 minutes is recommended.
3. Sterilize all equipment—barrel, sample cannula, target spacer, and forceps—before placing them on the aseptic bench.
4. Wipe the surface of the GDS-80 gene gun body and hose assembly with 70% ethanol before placing them inside the aseptic table.
5. Assemble the loading tube and sample loading tube, ensuring the gene gun is placed within the aseptic table and connected properly to the system.
6. Set the pressure regulator to 50 psi and confirm that the gas flow rate is approximately 10–15 L/min.
7. Prepare the DNA plasmid/gold powder suspension (0.5 µg DNA / 0.148 mg gold powder) just before the bombardment.
8. Use a 3 cm or 6 cm target spacer during the bombardment process, then transfer the sample to MS medium.
9. Incubate the sample for at least two days, followed by a one-day incubation in GUS staining solution.
10. Examine the results under a microscope.
**Results**
(a)
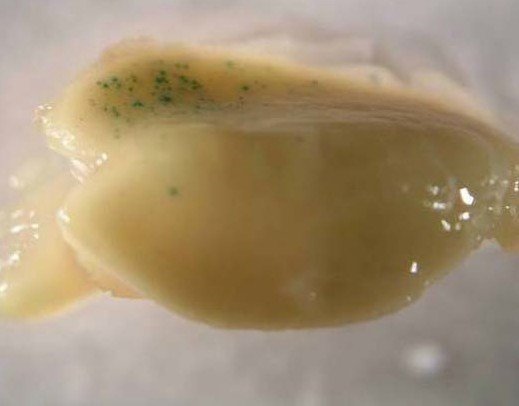
(b)

**Figure 1. Introduction of the GUS gene into corn embryos using a 3 cm target spacer at 50 psi.**
(a) Under normal, uncontaminated conditions
(b) In contaminated media
**Discussion**
Maintaining a sterile environment is crucial when working in an aseptic workstation. Any oversight can lead to contamination, which may compromise the results of the experiment (as shown in Figure 1). If the culture dish becomes contaminated, even if the DNA sample is free of contaminants, the GUS protein expression might be too low to detect.
Contamination can occur due to several factors, and proper precautions can help prevent it:
a. **Contamination from the gene gun equipment**:
When using the GDS-80 gene gun on the aseptic bench, it's easy to forget to fully sterilize the barrel and sample loading sleeve. Simply spraying 70% ethanol on the outer surface is not enough. Microorganisms can still remain on the inner surfaces of these parts. To avoid this, all components should be either autoclaved at 121°C for 30 minutes or soaked in 70% ethanol for over 20 minutes, then dried and placed in the aseptic table.
b. **Contamination from the sample itself**:
Plant samples collected from the field are often exposed to various microorganisms. It is essential to disinfect the samples before use. A common method involves soaking the sample in a solution containing bleach and Tween-20 for more than 20 minutes, followed by thorough rinsing with sterile distilled water. The sample should then be dried on a sterile petri dish before being transferred to the culture medium.
c. **Unskilled handling in the aseptic bench**:
Many people overlook critical steps when working inside the aseptic table. Always wash your hands thoroughly and disinfect them with 70% ethanol before entering the bench. Once inside, keep both hands within the workspace until the experiment is complete. If you need to move items in or out, disinfect your hands again before returning. Avoid opening the culture dish cover completely, and never let your hand or any object pass over the open dish. Always sterilize pipette tips before use and replace them after each sample. Use only sterilized forceps to handle the sample, and ensure they are flame-sterilized before each operation. If the sample falls on the bench, do not attempt to reinsert it into the medium.
d. **Poor maintenance of the aseptic table**:
The air filters in the aseptic bench should be replaced periodically, especially if their effectiveness decreases over time. Even with good maintenance, it's important to spray 70% ethanol on the working area inside the bench before each use.
All laboratory equipment must be properly sterilized before use. Contamination during the experiment is not acceptable. While each lab may have its own standard operating procedures (SOPs), the main goal remains the same: to prevent microbial contamination. Following the SOP carefully and paying attention to key steps can significantly reduce the risk of failure in plant transformation experiments.